

Metal carbides are one class of important high-performance material with excellent properties, including high hardness, high melting point, and good electrical conductivity. Among them, transition metal carbides have played an important role in modern industries because of their superior performance. This article will introduce metal carbides and 8 important transition metal carbide powders.
Metal carbides (Metallic Carbides) are inorganic compounds composed of metal and carbon elements. They exhibit high hardness, high melting point, good electrical conductivity, and chemical stability.
Metal carbides are compounds formed by the combination of metal atoms and carbon atoms. The carbon element usually exists in the form of an anion (C⁴⁻) and bonds strongly with metal ions. Depending on the metal element, the carbides can exhibit metallic, ceramic, or mixed characteristics.
The general chemical formula for metal carbides is:
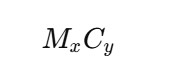
M represents a metal element (e.g., Ti, W, Ca).
C represents carbon.
x and y are integers indicating the ratio of metal to carbon.
Examples include:
The composition and properties of metal carbides allow for their division into four main types:
The first type is Transition Metal Carbides, including titanium carbide (TiC), tungsten carbide (WC) and tantalum carbide (TaC). These carbides have high hardness, high melting point, good conductivity and chemical stability, and are widely used in cutting tools, high temperature materials and coatings.
The other class is Main Group Metal Carbides. Some examples include calcium carbide (CaC₂) and beryllium carbide (Be₂C). These kinds of carbides are primarily ionic with relatively low hardness and can react with water, liberating the gas and thus often find applications as chemical raw materials or gas generators.
The third type is Metalloid Carbides such as silicon carbide (SiC) and boron carbide (B₄C). These carbides have extremely high hardness, high temperature resistance and chemical stability, and are widely used in abrasives, bulletproof materials and electronic component manufacturing.
The fourth type is rare Rare Earth Metal Carbides, typical examples of which include uranium carbide (UC) and thorium carbide (ThC₂). This kind of carbide has a high melting point, high density, and good thermal conductivity, and is mainly used in the high-temperature structural parts.
Different types of metal carbides have obvious differences in structure, properties and applications.
Transition metal carbides are highly regarded for their excellent properties. With advancements in 3D printing and nanomaterials, the application potential of transition metal carbides has further expanded. Below are some classic transition metal carbide powders:
Titanium carbide powder is a transition metal carbide composed of titanium and carbon, with the chemical formula TiC. It features high hardness, a high melting point (approximately 3160°C), and excellent chemical stability, typically appearing gray-black in color.
Owing to superior resistance to wear and electrical conductivity, it is extensively used in hard alloy, metal ceramics, and tool coating. In addition, TiC often acts as an added reinforcing phase in high-temperature structural materials to increase the strength and heat resistance of composites.
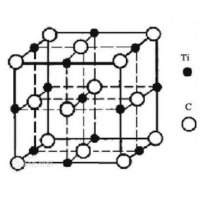
Fig 1. The structure of titanium carbide
Tungsten carbide powder is a hard material composed of tungsten and carbon, with the chemical formula WC. It has a hardness close to that of diamond, a high melting point of 2870°C, and excellent thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance.
It finds huge applications in producing hard alloy tools, drill bits, wear parts, and mining machinery tools. It is also an essential raw material for thermal spray coatings, which protect the surfaces of machinery and prolong service life.
When combined with cobalt, tungsten carbide powder forms Tungsten Carbide Cobalt powder, which combines high hardness with good toughness.

Fig 2. Components made of tungsten carbide
Tantalum carbide powder (TaC) is a high-melting-point carbide (3880°C) and one of the compounds with the highest known melting points. It exhibits excellent heat resistance, chemical inertness, and high electrical conductivity.
TaC powder is primarily used in aerospace applications, such as rocket nozzles, thermal protection coatings. Additionally, it serves as an additive in Cemented carbides to enhance wear resistance and oxidation resistance.
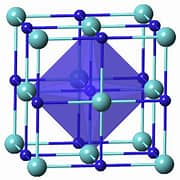

Fig 3. Molecular structure of tantalum carbide and Tantalum Carbide Ceramics
Niobium carbide powder is composed of niobium and carbon, with the chemical formula NbC. It is characterized by high hardness, a melting point of approximately 3600°C, and excellent corrosion resistance.
NbC powder is widely used as a hardening agent in the steel industry, as well as in cutting tools and abrasion-resistant materials. Besides its use in superconducting materials and high-temperature operating alloys, NbC acts to increase strength and thermal shock resistance.
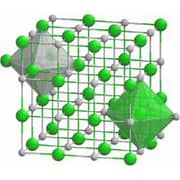
Fig 4. Molecular structure of niobium carbide
Vanadium carbide powder is a transition metal carbide composed of vanadium and carbon, with the chemical formula VC. It features high hardness, a melting point of approximately 2810°C, and good electrical conductivity, with relatively low density.
VC powder is normally used as a grain refiner in hard alloys and can greatly improve material hardness and toughness. The application fields are in high-temperature materials, metal ceramics, aerospace, and tool manufacturing.
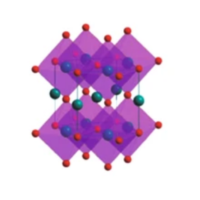
Fig 5. Structure of vanadium carbide
Hafnium carbide powder is a kind of ultra-high temperature carbide, which consists of hafnium and carbon. The chemical formula is HfC. It has the highest melting point among all the known materials, reaching 3958°C.
HfC powder is characterized by high hardness, excellent electrical conductivity, and chemical stability. It is widely used in aerospace, especially for rocket engine nozzles and thermal protection coatings. Besides, HfC is also applied as a reinforcement material to hard alloys and metal ceramics, which improves the performance of these materials under extreme conditions.

Fig 6. Hafnium Carbide Powder
Zirconium carbide powder, with the chemical formula ZrC, is a transition metal carbide composed of zirconium and carbon. It has a high melting point of 3550°C and is known for its high hardness, excellent heat resistance, and oxidation resistance.
ZrC powder is primarily used in high-temperature materials, such as refractories, rocket nozzles. It is also applied in metal ceramics and cutting tools to improve wear resistance and thermal shock performance.

Fig 7. Zirconium Carbide Powder
Molybdenum carbide powder is a transition metal carbide composed of molybdenum and carbon, with the chemical formula Mo₂C. It features a high melting point of 2687°C, high hardness, excellent catalytic properties, and good electrical conductivity and chemical stability.
Mo₂C powder is mainly used in catalyst applications, such as hydrodesulfurization and hydrogen evolution reactions, as a substitute for precious metals. It is also employed in wear-resistant materials, high-temperature structural components, and as a reinforcing phase in ceramic composites to enhance hardness and heat resistance.
Stanford Advanced Materials offers a wide range of carefully produced carbides in different grades for use in cemented carbides, wear-resistant components, high-temperature components, and thermal spray coatings.
|
Type |
Purity |
Shape |
Particle Size |
|
Titanium Carbide Powder |
99.50% |
Spherical |
10.0-60.0um |
|
Tungsten Carbide Powder |
≥99.8% |
Spherical |
0-25,15-53,45-105,75-150μm |
|
Tantalum Carbide Powder |
>99.0% |
0.5um to 2um |
|
|
Hafnium Carbide Powder |
99.90% |
-100 mesh +500 mesh/ as request |
|
|
Molybdenum Carbide Powder |
99.90% |
-100 mesh +500 mesh/ as requested |
|
|
Vanadium Carbide Powder |
>99.9% |
D 50: 0.8-1 um/ 3-5 um/ as requested |
|
|
Zirconium Carbide Powder |
99.50% |
D 50: 0.8-1 um/ 3-5 um/ as requested |
|
|
Tungsten Carbide Cobalt Powder |
99.90% |
Spherical |
0.85-0.005mm, or as request |
If you are interested, please Get A Quote and learn more details.

United States
.png)



