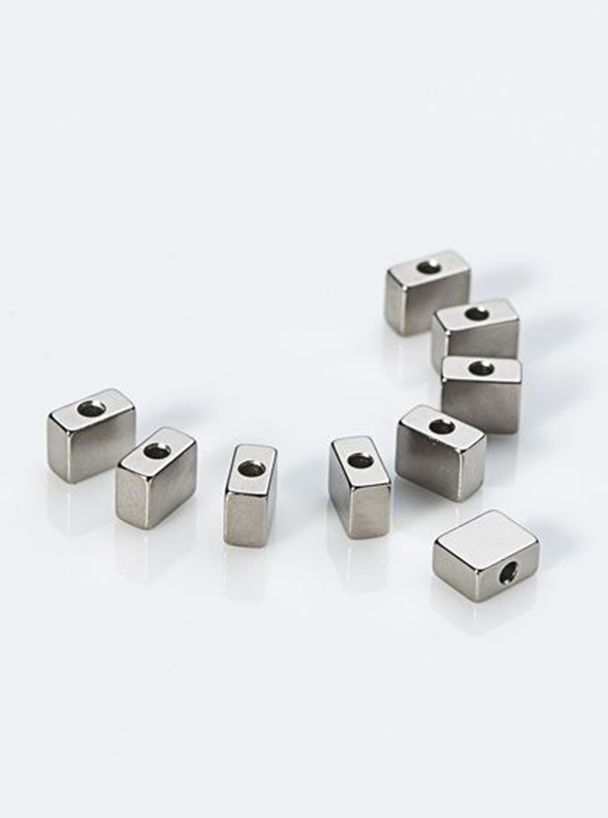
Metal powders are used in the manufacturing process of magnetic alloys, which are then sintered to create a crystalline structure that exhibits magnetic properties. The resulting magnetic alloy can be further processed to create magnets, sensors, and data storage devices. Examples of magnetic alloys include neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) and samarium-cobalt (SmCo), which are used to create powerful magnets.
Here are the most commonly used metal powders in magnetic alloys,
Including
- Iron - the most widely used magnetic metal due to its abundance, excellent magnetic properties, and low cost.
- Samarium-cobalt - known for its high magnetic energy product and high coercivity, making it useful in high-temperature applications, as well as in electric motors and generators.
- Alnico - valued by its high magnetic permeability and high coercivity, making them ideal for use in permanent magnets.
- Neodymium - utilized in neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) magnets, which have the highest magnetic energy product of any commercially available magnet.