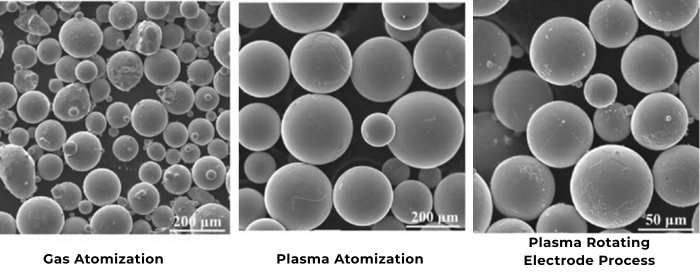
Titanium alloys are renowned for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and versatility in various industries. Among the diverse range of titanium alloys, Ti 6-4 Grade 5 and Ti 23 stand out for their unique properties and applications. In this blog, we'll delve into the key differences between Ti 6-4 Grade 5 and Ti 23, shedding light on their respective characteristics and best-suited applications.
1. Composition:
Ti 6-4 Grade 5: Ti 6-4 Grade 5, also known as Titanium 6-4, is a commonly used alloy composed of 90% titanium, 6% aluminum, and 4% vanadium. This combination results in a strong and heat-treatable alloy with excellent corrosion resistance.
Grade 23 Titanium: Grade 23 is a newer titanium alloy that combines 90% titanium, 6% aluminum, 2.5% vanadium, and 0.2% palladium. The addition of palladium enhances the alloy's corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, making it suitable for medical applications.
2. Strength and Toughness:
Ti 6-4 Grade 5: Ti 6-4 Grade 5 is renowned for its high strength and toughness, making it ideal for aerospace applications, marine components, and structural components in various industries.
Grade 23 Titanium: Grade 23 maintains the impressive strength of Ti 6-4 Grade 5 while incorporating palladium to enhance its toughness and corrosion resistance. This makes Grade 23 particularly suitable for medical implants and devices.
3. Corrosion Resistance:
Ti 6-4 Grade 5: Ti 6-4 Grade 5 exhibits excellent corrosion resistance in a variety of environments, including seawater, making it suitable for marine and offshore applications.
Grade 23 Titanium: Grade 23, with its added palladium content, offers superior corrosion resistance compared to Ti 6-4 Grade 5. This makes it an excellent choice for medical implants, where resistance to bodily fluids and corrosion is critical.
4. Biocompatibility:
Ti 6-4 Grade 5: While Ti 6-4 Grade 5 is biocompatible and has been used in certain medical applications, Grade 23 is specifically designed to enhance biocompatibility. The palladium addition in Ti 23 further improves its compatibility with the human body, making it a preferred choice for medical implants.
5. Applications:
Ti 6-4 Grade 5: Ti 6-4 Grade 5 finds applications in aerospace components, marine equipment, chemical processing, and various structural components where high strength and corrosion resistance are essential.
Grade 23 Titanium: Grade 23 is primarily used in the medical field for manufacturing surgical implants, dental devices, and other biomedical applications where biocompatibility and corrosion resistance are paramount.
The difference between Ti 6-4 (Grade 5) and Ti 6-4 ELI (Extra Low Interstitials) lies in their chemical composition, mechanical properties, and intended applications, particularly in the medical field. Let's explore the distinctions between these two titanium alloys:
1. Chemical Composition:
Ti 6-4 (Grade 5): Titanium 6-4, also known as Grade 5, consists of 90% titanium, 6% aluminum, and 4% vanadium. This alloy is widely used in aerospace, marine, and industrial applications due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and heat-treatable properties.
Ti 6-4 ELI: Ti 6-4 ELI is a variant of Ti 6-4 with Extra Low Interstitials. It has a similar composition, containing 90% titanium, 6% aluminum, 4% vanadium, but with reduced levels of interstitial elements (oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon). The lower interstitial content improves ductility and makes it more suitable for medical applications.
2. Mechanical Properties:
Ti 6-4 (Grade 5): Ti 6-4 exhibits high tensile strength, toughness, and excellent corrosion resistance. It is known for its favorable mechanical properties, making it suitable for demanding applications in aerospace and industrial engineering.
Ti 6-4 ELI: Ti 6-4 ELI shares similar mechanical properties with Ti 6-4 but is refined to have enhanced ductility. The lower interstitial content in ELI improves its cold formability, making it more suitable for medical implant manufacturing.
3. Applications:
Ti 6-4 (Grade 5): Ti 6-4 is widely used in aerospace components, marine equipment, chemical processing, and various structural applications where high strength and corrosion resistance are crucial.
Ti 6-4 ELI: Ti 6-4 ELI is specifically designed for medical applications due to its improved ductility and biocompatibility. It is commonly used for manufacturing surgical implants, dental devices, and other biomedical components.
4. Biocompatibility:
Ti 6-4 (Grade 5): While Ti 6-4 is biocompatible and has been used in some medical applications, Ti 6-4 ELI is specifically engineered for improved biocompatibility. The ELI variant is preferred for medical implants where the material comes into direct contact with the human body.
In conclusion, while both Ti 6-4 Grade 5 and Grade 23 Titanium share a common base composition, the addition of palladium in Grade 23 titanium sets it apart with enhanced corrosion resistance and biocompatibility. The choice between these titanium alloys ultimately depends on the specific requirements of the intended application, whether it be aerospace engineering, industrial components, or medical implants. Understanding these differences allows engineers and manufacturers to make informed decisions when selecting the most suitable titanium alloy for their particular needs.