

Molybdenum can maintain stability and strength at high temperatures, which is why its first application was as a filament in incandescent light bulbs. Additionally, molybdenum's wear resistance and corrosion resistance make it the preferred material for many applications.

The molybdenum powder comprises tiny particles of molybdenum, a fine grayish-black mass. It is reflected that molybdenum powder enjoys excellent mechanical and thermal properties due to its very high melting point of 2623°C (4753°F) and density of 10.22 g/cm3. Therefore, because of the power and strength of molybdenum powder, it finds a very high demand in various applications where temperature resistance is found to be extreme. It plays a vital role in applications, starting from electronics to aerospace, under conditions where materials have to work efficiently under extreme conditions.
| Type | Purity | Shape | Particle Size | |
| Molybdenum Powder | 99.80% | Spherical | ||
| Molybdenum Rhenium Alloy Powder | Rhenium 10.00-55.50% | 99.98% | Spherical | Customized |
| Mo 59%, Re 41% | 99.9%~99.999% | Non-Spherical | -200 Mesh or customized | |
| Mo52.5, Re47.5 | 99.00% | Non-spherical | -200 Mesh or customized | |
| Mo 55.5%, Re 44.5% | 99.00% | Non-spherical | -200 Mesh or customized | |
| Mo 58.5%, Re 41.5% | 99% | Non-spherical | -200 Mesh or customized | |
| Titanium Molybdenum Alloy Powder | 99.90% | Spherical | 0~45μm or customized | |
| Molybdenum Nickel Alloy Powder | Ni80Mo20 | 99.00% | Spherical | 40~50μm or customized |
| Ni10Mo90 | ||||
| Ni87.5Mo12.5 | ||||
| Molybdenum Carbide Powder | 99.90% | -100 mesh +500 mesh/ as requested | ||
| Tungsten Molybdenum Alloy Powder | ≥99.9% | Spherical | 5-25μm, 15-45μm, 15-53μm, 45-75μm, 45-105μm, 75-150μm |
|
Our ≥99.95% or 99.9% purity molybdenum powders are both spherical and non-spherical in shape, with particle sizes as small as 60nm. Our molybdenum alloy powders are supplied in molybdenum-rhenium (Mo-Re), molybdenum-nickel (Mo-Ni) and titanium-molybdenum (Ti-Mo) alloy forms.
Molybdenum has good thermal conductivity and a thermal expansion coefficient similar to that of silicon.
Molybdenum can resist corrosion from molten glass.
Molybdenum-rhenium alloys can maintain excellent strength and creep resistance at high temperatures.
Molybdenum powder can be used in steelmaking, and steel alloyed with molybdenum exhibits high strength, high toughness, outstanding heat resistance, and corrosion resistance.
As an alloying element in steel, molybdenum offers the following advantages:
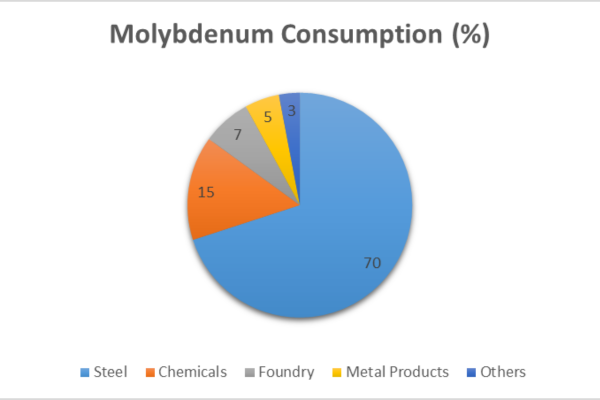
Molybdenum is mostly used in the steel industry, which makes up about 70% of its use. It is added to different types of steel to make them stronger, tougher, and more resistant to rust. About 15% is consumed in the chemical industry for things like petroleum catalysts, pigments, and lubricant additives. Another 7% goes to the foundry industry to improve the heat resistance and strength of cast iron and special castings. Metal products, like high-temperature alloys and electronic parts, also use about 5%. And the remaining 3% is used in other areas, such as medical devices, glass, and ceramics.
1. Molybdenum Metal Powder (99.0 Mo)
Molybdenum metal powder serves as the primary raw material for producing various molybdenum products. It is processed into desired forms using powder metallurgy techniques or thermal spraying.
2. Molybdenum-Rhenium Alloy Powder
The addition of rhenium significantly improves the plasticity, strength, and recrystallization temperature of molybdenum.
3. Molybdenum-Niobium Alloy Powder
The addition of niobium also enhances the strength and high-temperature performance of molybdenum while maintaining good processability.
4. Titanium-Molybdenum Alloy Powder
Here, "titanium-molybdenum alloy" typically refers to β-type titanium alloys with titanium as the base and molybdenum as the primary alloying element, with Ti-15Mo being the most typical example. It is commonly used in biomedical implants. The Ti-15Mo alloy offers excellent biocompatibility, a low elastic modulus, and outstanding corrosion resistance in bodily fluids. It is often used to manufacture artificial hip joints, femoral stems for knee joints, bone plates, bone screws, dental implants, and prosthetics.
5. Molybdenum Carbide Powder
Molybdenum carbide is a high-melting-point, hard ceramic material with platinum-like catalytic properties.

