Refractory metals generally have melting points in excess of 2000°C (3632°F). They have good mechanical strength, and high corrosion resistance. That allows them to maintain good mechanical properties under hot conditions. Principal refractory metals include tungsten (W), tantalum (Ta), molybdenum (Mo), Niobium (Nb), hafnium (Hf), Chromium (Cr), Vanadium(V), Zirconium (Zr), and Titanium (Ti). . .
The most common of these are tungsten, tantalum, molybdenum and niobium. Below we will outline the properties and applications of these four common resistant metals and their powder forms.
These refractory metals all have high melting points and are corrosion resistant, but they also have different properties. We’ll explore those differences.
Tungsten is a common refractory metal with a melting point of 3422°C. The silvery white color of tungsten gives it a metallic appearance.
Tungsten refractory metal has a low humidity and is slow. Not only is tungsten extremely hard, it is also chemically stable. Most acids and bases have some effect on tungsten.
Hydrogen, water, or concentrated acids do not react with tungsten at all. Tungsten decomposes only in aqua regia and in a 1:1 mixture of hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid.
Tantalum is a lightweight, high strength refractory metal with a melting point of 3017°C.
Chemically, tantalum refractory metal is extremely corrosion resistant. Incompatible with aqua regia, chromic acid, nitric acid, sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid under hot and cold conditions. However, it is soluble in hydrofluoric acid, fluoride compounds, and oxalic acid.
It can also combine with hydrogen to form hydrides, destroying its metallic properties and corroding it.
Molybdenum is a highly malleable metal, with a melting point typically around 2623 degrees Celsius.
At high temperatures, molybdenum refractory metal exhibits oxidizing properties. It oxidizes slowly up to 520°C and begins to oxidize faster than 600°C. However, at moderate or high temperatures at room temperature, molybdenum is suspended in air or water.
Molybdenum refractory metal has corrosion resistance. Only dilute hydrochloric acid and a 1:1 mixture of hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid produce corrosion.
Niobium refractory metal is at 2477°C and is a high-strength, low-melting metal.
Refractory Niobium has similar properties to tantalum, but with a difference: Niobium has a lower melting point and higher melting point than tantalum so niobium is rarely used as a heating element.
Niobium refractory metal has a strong affinity, making it particularly suitable as a getter for high temperature applications. It can also be used as a building material in vacuum systems.

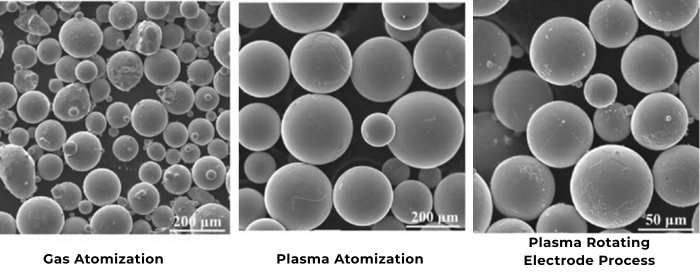
Fig 1. Refractory Metal Powder
Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) is at the forefront of powder development, providing high performance refractory metal powders. Including: tungsten powder, tungsten alloy powder, tantalum powder, tantalum alloy powder, molybdenum powder, molybdenum alloy powder, niobium powder, niobium alloy powder. To learn more about these refractory powders, please feel free to contact us and check out our homepage.
The unique properties described above make these refractory powders important in many high-temperature and high-performance applications. Below, we compare the use of these four metals in modern Industries.
1. Light: Tungsten powder is widely used in incandescent bulb fibers because of its high temperature and excellent electrical conductivity.
2. Electrical contacts: Tungsten powder is also used in the manufacturing of electrical contacts for high-current applications. Because of its high melting point and resistance to electrical arcing, tungsten powder is ideal for use in electrical switches, relays, and circuit breakers.
3. Medical Devices: Tungsten powder is used in radiation shielding materials for medical cameras and cancer treatment devices.
4. Thermal Spray Coatings: Tungsten powder can be used in thermal spray applications to create wear-resistant coatings. The powder is heated and propelled onto a surface, forming a dense and durable coating that protects against erosion, corrosion, and wear.
1. Electronics: Tantalum powder capacitors are important in smartphones, computers, and other electronic devices because of their high durability and reliability.
2. Medical implants: Tantalum’s biocompatibility makes it ideal for implant surgeries, such as hip replacements and orthopedic devices.
3. Chemical Uses: Tantalum powder is used in corrosive handling equipment such as reactors and heat exchangers due to its corrosion resistance.
4. Jewelry: Tantalum powder is used in the production of high-quality jewelry. It is known for its attractive dark grey color and is often used as an alternative to platinum. Tantalum jewelry is durable, scratch-resistant, and hypoallergenic.
1. Alloys: Refractory molybdenum powder is a key alloying element in steel, enhancing strength, hardness, and resistance to wear and corrosion. It is commonly found in stainless steel and other high-strength alloys.
2. Electronics: Used in the manufacture of thin films for semiconductor devices and LCD screens.
3. High-Temperature Furnaces: Refractory molybdenum components are used in high-temperature furnaces and vacuum environments due to their stability at elevated temperatures.
4. Solar cells: Molybdenum powder is used as a back electrode in thin-film solar cells. It helps improve the efficiency and durability of the solar cells.
1. Steel Additive: Refractory niobium powder is added to steel for strength, durability and resistance to high temperatures. It is widely used in the automotive and manufacturing industries.
2. Aerospace: Niobium is used in aircraft engines and rocket parts because of its high melting point and high melting point.
3. Optical Coatings: Niobium metal powder is used in the production of optical coatings, which are applied to glass and other materials to enhance their reflective and anti-reflective properties. These coatings are used in lenses, mirrors, and other optical devices.
Table 1. Refractory Metal Powder Applications Comparison
.png)
Table.1 compares the common applications of refractory metal powders, such as, tantalum (Ta), tungsten (W), molybdenum (Mo), and niobium (Nb).
Refractory metals play an important role in various high temperature and high-performance applications because of their unique properties.
Their unique texture, high mechanical properties and corrosion resistance make these refractory powders important in a wide range. These industries rang from electronics to aerospace, medical devices and other applications. That reaffirms its importance in today’s industry and innovation.
Related Articles:
Iron Powder in Aerospace: Enhancing Performance and Reducing Weight