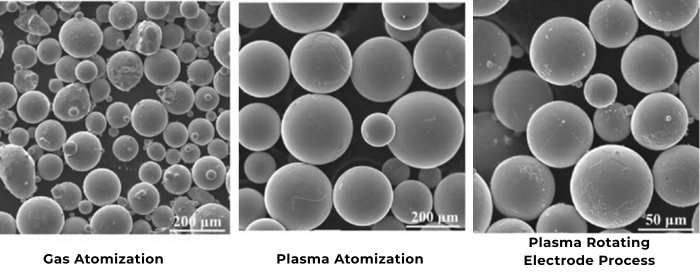
Metal powders play an important role in the semiconductor industry. Their unique physical and chemical properties make them essential in applications ranging from conductivity to heat dissipation. By categorizing them based on their uses, we can better understand their diverse contributions to the semiconductor field.
The conductivity ability is one of the main factors in semiconductor manufacturing when considering device performance. Among them, silver and copper powders stand out for their unique properties and versatility.
Silver powder is used extensively in solar cell electrodes and conductive paste because of its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity. According to the low resistivity, the metal is an ideal candidate for various high-efficiency electronic devices. Besides, corrosion resistance makes it durable under tough conditions.
Copper powder is an important material in conductive applications due to its high conductivity and cheapness. It is widely used in printed circuit boards and chip interconnections. It is less corrosion-resistant than silver, but appropriate surface treatments enhance its performance in many applications.
It is mainly used in high-reliability applications, such as connectors and contacts in advanced chips. Due to its excellent conductivity and resistance to corrosion, the device will surely need it for precision and stability.
Nickel powder is moderately conductive and resists corrosion well. It can be used in nickel-based conductive pastes and coatings. Its low cost and effectiveness make it popular in middle-class electronic equipment.
Metal powders resolve heat dissipation issues in high-power semiconductor devices and electronic equipment. Representative materials, such as aluminum, molybdenum, and tungsten powders, possess superior performance in effectively dissipating heat under extreme conditions with stability.
Aluminum powder is light, with high thermal conductivity, and finds usage in heat sinks and thermal composites. Its low mass density brings a reduction in weight for devices, with substantial congruence to optimal heat dissipation; hence, it is a favorite for thermal management applications.
Molybdenum powder is used in substrates for heat dissipation of high-power chips with its high melting point and good thermal conductivity. It is highly stable even under extreme temperatures, ensuring its reliability in advanced semiconductor devices.
Tungsten powder has superior performances in thermal conductivity and stability at high temperatures, making it highly suitable for use in high-power electronic devices. It reliably operates under extreme conditions, hence being one of the best choices for thermal management.
Soldering and interconnection are crucial in semiconductors, and the usage of metal powders is immense in this field. Among the most used powders are those of tin, indium, and silver due to their importance in making efficient and reliable connections.
Tin powder is a key ingredient in solder pastes and welding materials. Its low melting point enables efficient soldering, making it suitable for various manufacturing processes.
Indium powder excels in low-temperature soldering and flexible device connections. Its unique flexibility and low melting point make it ideal for high-precision and temperature-sensitive applications.
Silver powder, with its high melting point and thermal conductivity, is a reliable choice for high-performance soldering materials. It is particularly effective in applications requiring temperature stability.
Of all, molybdenum powder, tungsten powder, indium powder, and titanium powder are the most common choice in thin film preparation. After processed through specific processes, the metal powders form thin film layers widely used in chip interconnection, transparent conductive films, and surface protection of semiconductor devices.
Molybdenum powder is one of the core basic materials in semiconductor thin-film production. High conductivity and excellent heat resistance make it widely used in the manufacture of transistors and displays.
Tungsten powder is used in chip interconnection layers. The high density and low thermal expansion rate ensure stable performance in high-power devices.
Indium powder plays a very important role in the production of transparent conductive films such as ITO films. These films are very crucial in displays touchscreens and solar cells because of their transparency and conduction.
Titanium powder finds wide application in high-performance oxide films. The films exhibit excellent optical and mechanical properties and act as protection for semiconductor devices.
Metal powders used in capacitors and functional materials mainly include tantalum and zinc powders.

Tantalum powder is the main material composing tantalum capacitors, which have a high dielectric constant for use in compact and high-performance electronic components. Tantalum capacitors have great stability and efficiency in semiconductor applications.
Zinc powder is widely used in producing transparent conductive materials such as zinc oxide films, which are ideal for electronic coatings and transparent devices owing to their excellent properties at low costs.
Metal powders are extensively and deeply applied in the semiconductor industry due to their unique characteristics. They play a significant role in conductivity, heat dissipation, soldering, thin film production, and functional materials. The value of metal powders in the semiconductor sector is summarized in brief in Table 1.
Table1. Uses of Metal Powders in Semiconductors
|
Application |
Metal Powder |
Specific Application |
|
Conductive Materials |
Silver Powder |
Solar cell electrodes and conductive paste |
|
Copper Powder |
PCB and chip interconnects |
|
|
Gold Powder |
High-end chip connectors and contacts |
|
|
Nickel Powder |
Nickel-based conductive paste and coatings |
|
|
Thermal and Heat Dissipation Materials |
Aluminum Powder |
Heat sinks and thermal materials |
|
Molybdenum Powder |
High-power chip heat dissipation substrates |
|
|
Tungsten Powder |
High-power device heat dissipation |
|
|
Soldering and Interconnection Materials |
Tin Powder |
Chip and PCB soldering |
|
Indium Powder |
Low-temperature soldering and flexible device connections |
|
|
Silver Powder |
High-temperature soldering materials |
|
|
Thin Film Materials |
Molybdenum Powder |
Transistor and display thin films |
|
Tungsten Powder |
Chip interconnect layers |
|
|
Indium Powder |
Transparent conductive films (ITO) |
|
|
Titanium Powder |
Protective films for semiconductor devices |
|
|
Capacitors and Functional Materials |
Tantalum Powder |
Core material for tantalum capacitors |
|
Zinc Powder |
Transparent conductive materials and coatings |