

Duplex stainless steel powder is a metal material composed mainly of two phases: austenite and ferrite. This unique structure gives the material excellent properties found in both austenitic and ferritic stainless steels, such as high strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and good weldability.
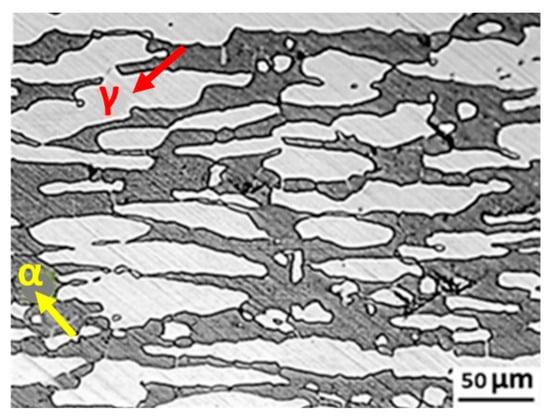
Fig 1. Typical microstructure of a duplex stainless steel
As a well-known metal powder supplier, Stanford Advanced Materials(SAM)provides high-quality spherical duplex stainless steel powder. Table 1 shows the typical chemical composition of duplex 2205 and 2507, while Table 2 presents their mechanical properties.
Table 1. Chemical Composition % of Duplex Powder (2205, 2507)
| Grade | Fe | Cr | Ni | Mo | C | Si | Mn | P | S | N | Cu |
| 2205 | ≥74 | 22 | 5 | 3.2 | ≤0.03 | ≤1.0 | ≤2.0 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.015 | 0.18 | / |
| 2507 | ≥60.3 | 25 | 7 | 4 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.8 | ≤1.2 | ≤0.025 | ≤0.8 | 0.3 | 0.5 |
Table 2. Physical and Mechanical Properties of 2205, 2507
| Grade | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength 0.2% (MPa) | Elongation % | Hardness (HB) MAX |
| 2205 | 620 | 448 | 25 | 217 |
| 2705 | 795 | 550 | 15 | 310 |
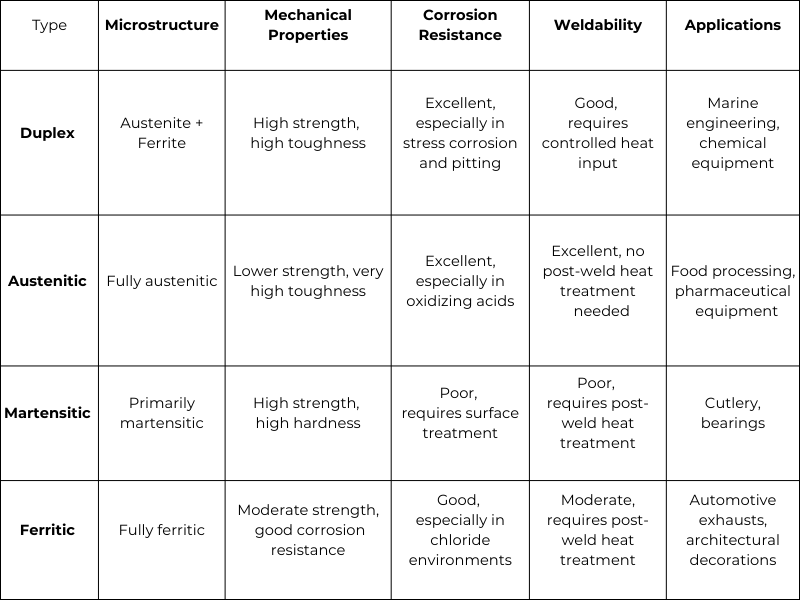
Selecting the right stainless steel powder—whether duplex, austenitic, martensitic, or ferritic—depends on specific application requirements and environmental conditions. The characteristics and application scenarios of each type are summarized in Table 3 to assist in making the right choice.
Duplex stainless steel powder combines austenite and ferrite microstructures, offering high strength and toughness with excellent corrosion resistance, particularly against stress corrosion and pitting. It has good weldability, though controlled heat input is required, making it ideal for applications like marine engineering and chemical equipment.
Austenitic stainless steel powder is fully austenitic, providing lower strength but very high toughness. It excels in corrosion resistance, especially in oxidizing acids, and has excellent weldability without the need for post-weld heat treatment. This type is commonly used in food processing and pharmaceutical equipment.
Martensitic stainless steel powder is primarily martensitic, known for its high strength and hardness but poor corrosion resistance, which often requires surface treatments. Its weldability is poor, necessitating post-weld heat treatment. It is typically used in applications such as cutlery and bearings.
Ferritic stainless steel powder is fully ferritic, offering moderate strength and good corrosion resistance, particularly in chloride environments. Its weldability is moderate, often requiring post-weld heat treatment, and it is used in automotive exhausts and architectural decorations.
Table 3. Properties and Applications Comparison of Duplex, Austenitic, Martensitic, and Ferritic Stainless Steel Powders
Duplex stainless steel powder has a wide range of applications. It can be processed cold and hot and formed and has good weldability. Therefore, it is very suitable for making oil well pipes, chemical storage tanks, heat exchangers, condenser coolers, and other pressure equipment that are prone to pitting and stress corrosion. The following are specific industries:
1. Marine Engineering
Duplex stainless steel's excellent corrosion resistance makes it highly suitable for marine environments. Through additive manufacturing, complex ship components, offshore platform structures, and underwater equipment can be produced more quickly and flexibly.
2. Energy Industry
In the oil and gas industry, duplex stainless steel is used to manufacture pipe fittings, valves, and pump bodies, which require corrosion resistance and high strength. Additive manufacturing can produce customized, optimally designed parts, reducing material waste and production time.
3. Aerospace
The lightweight design advantage of additive manufacturing makes duplex stainless steel powder highly promising for producing high-performance, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant aerospace components, such as turbine blades and structural supports.
4. Medical Devices
The strength and corrosion resistance of duplex stainless steel makes it suitable for manufacturing implants and surgical tools. Additive manufacturing enables the production of complex, precise, and customized medical devices.
.png)
Fig 2. Oil well pipes
Despite the significant advantages of duplex stainless steel powder in additive manufacturing, there are still several challenges in its practical application. These challenges mainly focus on powder quality control, process parameter optimization, residual stress and warpage management, and cost issues.
Firstly, controlling the quality of the powder is crucial. The quality of duplex stainless steel powder, including particle size distribution, oxide content, and flowability, directly affects the performance of the final parts. Ensuring consistency in powder quality is a major challenge, especially in large-scale production. Any slight inconsistency can lead to significant performance differences, particularly in high-demand applications.
Secondly, optimizing process parameters is also complex. During additive manufacturing, duplex stainless steel may develop uneven microstructures due to rapid cooling and solidification, such as uneven phase distribution. This phenomenon can impact the final material properties, necessitating precise control of process parameters to ensure uniform microstructures and optimized material performance. However, this process is complex and challenging to master fully.
Furthermore, residual stress and warpage are unavoidable issues. During additive manufacturing, localized heating and cooling can cause residual stress and warpage in duplex stainless steel parts, affecting dimensional accuracy and mechanical performance. To mitigate this effect, additional heat treatment and post-processing are usually required, increasing manufacturing complexity and costs.
Finally, cost remains one of the main barriers to additive manufacturing. High-quality duplex stainless steel powder and additive manufacturing equipment are expensive, particularly in small-batch production, leading to high initial investment and production costs. This can limit its widespread application in certain fields. Nevertheless, as technology advances and economies of scale improve, cost issues are expected to gradually be alleviated.
Duplex stainless steel powder holds great promise in various industries due to its exceptional mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. However, successful application in additive manufacturing requires overcoming significant challenges, particularly in quality control, process optimization, and cost management. As the technology continues to evolve, duplex stainless steel powder is poised to play a pivotal role in advancing additive manufacturing applications across multiple sectors.
In addition to high-performance spherical stainless steel powders (including duplex, austenite, martensite, and ferrite), Stanford Advanced Materials also has spherical nickel, cobalt, titanium, tantalum, aluminum, and other metal and alloy powders. For more information, please visit the relevant page or get a quote from us.
Related reading:
Stainless Steel Powder: 301 vs. 304 vs. 316
Reference:
[1]. Gatto ML, Santoni A, Santecchia E, Spigarelli S, Fiori F, Mengucci P, Cabibbo M. The Potential of Duplex Stainless Steel Processed by Laser Powder Bed Fusion for Biomedical Applications: A Review. Metals. 2023; 13(5):949. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13050949

United States
.png)



