

With the rapid development of the Electric Vehicle (EV) industry, the importance of batteries as its core component has become increasingly prominent. The performance, cost, and lifespan of EV batteries largely depend on the quality of their upstream raw materials. This article provides a detailed overview of the key powder materials required in the production of EV batteries.
Currently, lithium batteries are the mainstream power choice for new energy vehicles. Lithium, as a key element in EV batteries, is supplied primarily in powder form. Common lithium powders include lithium carbonate (Li₂CO₃) and lithium hydroxide (LiOH·H₂O).
Lithium Carbonate (Li₂CO₃) is a raw material for manufacturing various lithium-based cathode materials (such as LiFePO₄, LiCoO₂, NCM). It provides the necessary lithium ions for the battery, which are crucial for energy storage. High-purity lithium carbonate ensures stable performance of cathode materials, improving the battery's energy density and cycle life.
Lithium Hydroxide (LiOH·H₂O) is mainly used in the production of high-nickel cathode materials (such as NCA LiNiCoAlO₂). It enhances the battery's energy density and cycle life by combining with high-nickel materials. In high-performance batteries, lithium hydroxide helps improve overall performance and stability.
Cobalt is primarily used in EV batteries to manufacture high-energy-density cathode materials. Cobalt oxide (Co₃O₄) is a common form of cobalt powder, typically obtained through the roasting and oxidation of cobalt ore. Cobalt oxide is widely used in the production of lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO₂) and lithium nickel cobalt aluminum oxide (NCA), enhancing the battery's stability and energy density. Another important cobalt compound is cobalt carbonate (CoCO₃), which serves as an intermediate for cathode materials and is further processed to form the final active substance.
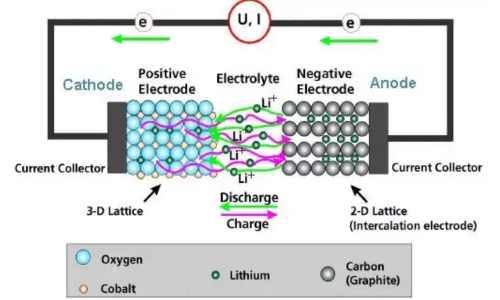
Fig 1. Role of Cobalt in Batteries: Increases energy density.
Despite its importance, cobalt faces a challenging reality. It is estimated that in 1 ton of lithium cobalt oxide, the lithium content is only 0.07 tons, while the cobalt content is 0.61 tons, more than 8 times that of lithium. However, cobalt's abundance in the Earth's crust is only one-sixth that of lithium. Given its high cost and safety concerns (poor thermal stability), manufacturers are striving to reduce cobalt usage in batteries. Elon Musk has stated that Tesla aims to reduce cobalt usage from 3% to 0%. Currently, increasing the nickel content in ternary lithium batteries is an industry consensus.
Nickel also enhances energy density and cycle life, and importantly, it is inexpensive. Nickel oxide (NiO) is the primary form of nickel powder, mainly used in the production of NCM (lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide) and NCA cathode materials. Nickel hydroxide (Ni(OH)₂) is a precursor for nickel-based cathode materials, ensuring high performance and consistency.
Manganese plays a significant role in the production of EV batteries. Its inclusion reduces battery costs while improving thermal stability and safety.
Manganese-based materials are sometimes used as conductive additives or surface coatings to enhance electrode conductivity and structural stability, such as nano-manganese oxide and manganate, which improve the conductive network and interface compatibility of electrode materials.

Graphite is a commonly used anode material in EV batteries. It comes in two forms: natural graphite powder and synthetic graphite powder.
Natural Graphite Powder, obtained by mining natural graphite ore and crushing/sieving, it is mainly used in standard anode materials. This natural material is responsible for the intercalation and deintercalation paths of lithium ions, affecting the battery's capacity and lifespan.
Synthetic Graphite Powder is produced through methods like chemical vapor deposition (CVD), offering higher purity and uniform particle size. This makes it suitable for high-performance batteries by improving consistency and cycle stability.
In addition to the aforementioned compound powders and graphite powders, certain metal powders are also used in EV battery production. Copper powder and aluminum powder are important components of electrode current collectors, supplied in powder form.
These metal powders ensure the overall conductivity of the electrodes, facilitating efficient energy transfer in the battery.
Functional additives are used in EV batteries to enhance performance and safety. Aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) and zinc oxide (ZnO) are common additive powders.
These additives optimize the battery's internal structure and chemical environment, extending its lifespan and enhancing overall performance.
Lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese are critical for cathode materials, each contributing to energy density, stability, and cost-effectiveness. Meanwhile, graphite is essential for anode materials, influencing battery capacity and lifespan. What’s more, metal powders (copper and aluminum) ensure efficient energy transfer in electrodes. Apart from it, additives (Al₂O₃, ZnO) enhance battery performance, safety, and longevity.
Stanford Advanced Materials (SAM) offers a variety of powder materials for EV battery production, including lithium, cobalt, nickel, graphite, copper, aluminum, aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃), and zinc oxide (ZnO). If you have related ordering needs, please feel free to obtain more information from our sales representatives through "Get A Quote" or "Leave A Message".
Table 1. which powders are used in EV batteries
|
Material |
Forms |
Role in EV Batteries |
Applications |
|
Lithium |
Lithium Carbonate (Li₂CO₃), Lithium Hydroxide (LiOH·H₂O) |
Provides lithium ions for energy storage, enhances energy density and cycle life. |
Cathode materials (LiFePO₄, LiCoO₂, NCM, NCA). |
|
Cobalt |
Cobalt Oxide (Co₃O₄), Cobalt Carbonate (CoCO₃) |
Increases energy density, improves stability. |
Cathode materials (LiCoO₂, NCA). |
|
Nickel |
Nickel Oxide (NiO), Nickel Hydroxide (Ni(OH)₂) |
Enhances energy density and cycle life, cost-effective. |
Cathode materials (NCM, NCA). |
|
Manganese |
Manganese Oxide (MnO₂), Manganese Carbonate (MnCO₃) |
Reduces costs, improves thermal stability and safety. |
Cathode materials (LiMn₂O₄, NCM). |
|
Graphite |
Natural Graphite, Synthetic Graphite |
Anode material, responsible for lithium-ion intercalation/deintercalation. |
Anode materials for standard and high-performance batteries. |
|
Metal Powders |
Copper Powder, Aluminum Powder |
Ensures electrode conductivity, lightweight, and high conductivity. |
Current collectors for anode (copper) and cathode (aluminum). |
|
Additive Powders |
Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃), Zinc Oxide (ZnO) |
Enhances stability, prevents side reactions, improves cycle performance. |
Solid electrolytes, electrode coatings, interface regulation. |

United States
.png)



